The Challenge
Circular economy aims to eliminate waste through the continual use of resources versus the traditional linear economy of “take, make, waste”. Circularity can be achieved through many means such as reducing, recycling, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and remanufacturing. Our client, a leading provider of bio-fuels and sustainable aviation fuel, is tackling two of the behemoths of un-sustainability – what to do with municipal solid waste (i.e., household and similar garbage) and how to decarbonize the aviation industry.
Pandemic impact aside, aviation is a growing industry and with that growth comes an increased carbon footprint. While solutions like electrified airplanes are being assessed, our client seeks to provide a near-term solution to cut emissions from flying through its commercially available sustainable aviation fuel. In order to do so, our client requested our support in identifying opportunities in the untapped Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) streams. The aim was to expand its feedstock and meet increasing demand from the aviation industry.
The key objectives of our client included:
• To understand the MSW value chain (waste collection, sorting, recycling, pre-treatment, disposal) unique to each city under study, including technologies used, industry participants, waste composition assessment, cost structure (variable and fixed cost analysis for indicative profitability assessment), and regulations.
• To identify potential partners across the most relevant cities and build an efficient business model in each geography.
Our Solution
We are following the fundamentals of our GREEN Framework, designed to generate insights to support decarbonization initiatives from strategy formulation to market execution.
Our team drilled down to create an MSW value-chain assessment to study opportunities across different nodes and geographies that leveraged benchmarking to identify, compare and prioritize the top prospective cities.
In the first stage – Generate – we combined secondary research, interviews across the waste value-chain, and expert validation to recommend efficient and dynamic waste business models.
In the next phase – Refine – we assessed critical MSW stream parameters relevant to the client at each step of the waste value chain; relevant parameters included availability of mixed and residual waste, and refuse-derived fuel (RDF), and solid recovered fuel (SRF) with indicative forecast for the next 5-10 years, material composition, rejects from pre-treatment processes, key technologies, partnerships, contracts, and indicative profitability at each step of the waste value chain.
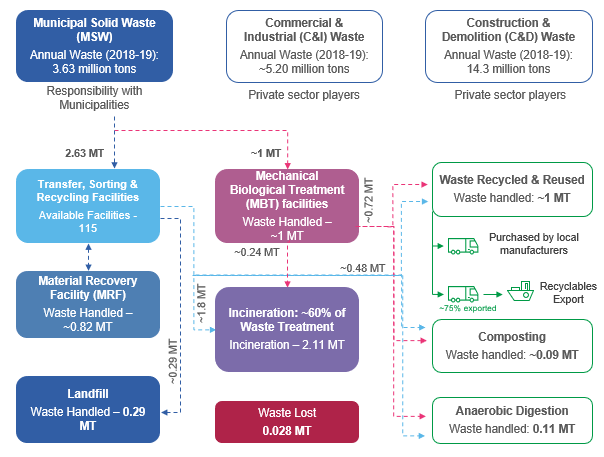
City: MSW Mass-Flow and Value-Chain
The city generates nearly 3.6 million tons of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW). Currently, around 60% is being incinerated
In the final stage – Equip – we built a list of potential partners and worked with the client to identify the most relevant ones by profiling shortlisted partners with critical requisite information such as access to MSW, RDF availability, and potential opportunities.
Business Impact
Improved time-to-market
The client gained deep insights into available opportunities and a shortlist of prospective partners across the untapped MSW value chain that enabled partner discussions and active engagement with potential partner cities.
Tangible business insights
The client developed a robust understanding of possible business models and market entry strategy in each of the shortlisted cities.
Scaling of methodology
The client is scaling the methodology to assess the value chain of other relevant waste streams (e.g., recycled wood) for the production of sustainable fuel.
Talk to One of Our Experts
Get in touch today to find out about how Evalueserve can help you improve your processes, making you better, faster and more efficient.