Rising federal rates, explosive inflation, and mounting debt are lending industry trends that have severely impacted the financial situation in the U.S.. The Fed began its rate hike campaign against high inflation in March 2022, taking the policy rate from near zero to 5.25% - 5.50% as of July 2023. In 2022, the banks benefited from an initial boost to interest income fueled by increasing interest rates, but challenges relative to declining loan growth, increased funding costs, and decreased liquidity started to become evident in the first quarter of 2023. Banks tightened credit standards on all types of business and consumer loans, demand for most loans weakened, and growth for all types of loans slowed.

After prolonged rate increases up to July 2023, the Fed has maintained the overnight rate at the current range of 5.25% - 5.50%, marking the May 2024 meeting as the sixth consecutive meeting where the policyholders have opted to hold rates steady. The Fed remains committed to moderating long-term inflation towards the central bank's 2.0% target to maintain price stability (current inflation at 3.3%). As per the Fed, the exact timing of potential rate cuts has been left open and will depend on the incoming data, the evolving outlook, and the balance of risks.
Beginning in June, the Committee has slowed the decline of its securities holdings by reducing the monthly redemption cap on Treasury securities from $60 billion to $25 billion, meaning that the Fed will lower the pace at which it withdraws liquidity from the system.
Inflation has continually impacted the U.S. economy, and lenders are also highly focused on the economic impact of the upcoming presidential election in November. Lender’s expectations for the U.S. economy's performance in the longer term, beyond six months, have increased significantly. Despite this optimistic outlook, volatility in borrower performance and an increase in bankruptcies is expected to continue until the Fed starts reducing interest rates and the presidential elections are decided. The upcoming elections also add to uncertainty around economic policies as substantial shifts are expected in key policies, including taxation, healthcare, entitlements, and regulations if the executive branch transitions from one party to another. Key issues currently at stake include U.S. engagement overseas, restrictions on trade and capital flows, immigration, support for Ukraine, and NATO commitments.
As per the Federal Reserve survey of senior bank lending officers conducted in April 2024, U.S. banks continue to tighten underwriting standards, more so on commercial loans than consumer loans. Reasons cited for tightening standards on commercial & industrial (C&I) loans are a less favorable/more uncertain economic outlook, reduced tolerance for risk, and worsening of industry-specific problems. In the first quarter of 2024, demand for commercial, industrial, and consumer loans declined slightly faster, reversing the improving trend that occurred in the second half of 2023.
Weakened demand for commercial & industrial loans is attributable to decreased customer financing needs for merger or acquisition and inventory and decreased customer investment in plant or equipment.
For all commercial real estate (CRE) loan categories, banks reported tightening all queried lending policies, including the spread of loan rates over the cost of funds, maximum loan sizes, loan-to-value ratios, debt service coverage ratios, and interest-only payment periods. Reasons for tightening standards on CRE loans were uncertain outlooks for CRE market rents, vacancy rates, and property prices. Weakened demand for CRE loans was mainly due to increased interest rates, decreased customer acquisition or development of properties, and a less favorable customer outlook for rental demand.
CRE exposures of regional banks have been heavily scrutinized since New York Community Bancorp reported a surprise loss and slashed its dividend in January 2024, citing loan loss provisions on CRE loans, which triggered a sell-off in U.S. regional banking CRE shares. Banks have been reassessing their business models and exiting/consolidating certain businesses. As per M&T bank's CFO Daryl N. Bible, "We are off to a solid start in 2024 as we were able to grow certain sectors of our commercial and consumer loan portfolios while continuing to shrink our commercial real estate exposure".
Additionally, in March 2024, S&P Global downgraded its outlooks on five regional U.S. banks - First Commonwealth Financial, M&T Bank, Synovus Financial, Trustmark, and Valley National Bancorp, to "negative" from "stable" due to their high commercial real estate (CRE) exposures.
Demand weakened for all residential real estate (RRE) loan categories. In addition, banks reported tighter standards and weaker demand for home equity lines of credit (HELOCs). Moreover, standards reportedly tightened for credit card, auto, and other consumer loans, and demand weakened. Tightened standards on consumer loans included increasing minimum credit score requirements for credit card, auto, and other consumer loans.
It is easy to conclude that the lending industry is undergoing a huge transformation driven by these changing market dynamics and technology. Below are key lending industry trends in the U.S. in 2024.
1. Banks are adopting digital innovation and artificial intelligence to offer personalized solutions and bring efficiencies in traditional loan processes
Borrowers are seeking personalized solutions, driving lenders to utilize data-driven insights to meet customers evolving needs. Banks are now developing digital platforms that enable faster and more efficient credit risk management processes. The adoption of these digital capabilities will not only optimize customer experience but will also bring efficiencies to traditional processes. Borrowers also demand that there should be transparency around the entire process, i.e., they should be able to track the entire loan process – from sales to origination to servicing.
As per the Dragonfly Financial Technologies "2024 State of Banking" survey, banks face an ever-growing list of new technologies and run the risk of trying to deploy too many new technologies too quickly. Prioritization will be key, and the survey broadly identified various services listed below that will make the banks more attractive to business and corporate customers and drive their business goals.

Banks leverage advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze large amounts of data in real time, identifying trends and patterns that may indicate credit risk. In particular, automation and technology-enabled cost reduction can improve transparency, generate efficiencies by reducing friction costs, such as commissions and fees related to transaction execution, and improve productivity levels, which will, in turn, lead to higher profitability. Other advancements, such as blockchain technology and transitioning to the cloud, are also gaining momentum in the U.S. lending industry.
Major U.S. banks have already started dabbling with generative AI programs, as per the research conducted by Accenture on the impact of generative AI across industries. It became apparent that while generative AI is likely to dramatically improve the efficiency of the banking operating model, its potential to differentiate and drive growth by enhancing the customer experience. The financial projections indicate that the gains over the coming years will be substantial for the early adopters:

Banks in the U.S. are now finding ways to incorporate AI for making lending decisions; for instance, M&T Bank, which is the sixth largest commercial bank in North America, will use the Rich Data Co. (RDC) AI platform to gain more comprehensive insights into cash flow health, credit risk, and lending opportunities. The bank will also use the platform to help detect early warning signs, access additional insights when making decisions during the customer relationship lifecycle, and enhance its risk management and lending strategies. JP Morgan has also implemented an AI and machine learning-powered Contract Intelligence (Coin) platform through which the bank has automated the review of commercial loan agreements.
Swarup Pogalur, Wells Fargo's head of digital and AI capabilities engineering, said, "AI Products and Solutions and the AI technology landscape is going through a phase of rapid innovation and has opened up a wealth of opportunities to reimagine how we engage with our customers and employees by enabling personalized and intuitive experiences," he added "At Wells Fargo, we've been on a journey to AI adoption — from a digital adopter to a digital leader — while carefully managing our risks to ensure consistency with regulatory oversight."
"We are thinking about how AI can help us better serve our clients," said Aditya Bhasin, Bank of America's (BofA) Chief Technology and Information Officer. BofA now has 6,600 granted patents or pending applications worldwide, including more than 800 related to AI. According to BofA CEO Brian Moynihan, AI and blockchain will be among the two technologies in which the bank will invest its $3.8 billion innovation budget this year.
2. Traditional banks are competing in the space of new sources of financing, such as private credit
Banks are competing with new forms of lending and business support, including fintech companies and alternative lenders. Fintech companies have opened avenues for banking and financial institutions to innovate. Using advanced analytical tools, fintech players have enhanced customer service by decreasing the cost and time for loan applications, approvals, and disbursals. The North American fintech market is expected to be valued at $212.3 billion by 2029 from $71.0 billion in 2024 and grow at a CAGR of 24.5% from 2024 to 2029. As per a report published by Fortune Business Insights, North America is leading the fintech market share globally, with Banks being the dominating end-users with a 40.0% share. Fintech innovation, a growing need for customization, regulatory compliance, and cross-selling opportunities are key factors driving the region's fintech market growth.
Alternative lending, including private credit, marketplace lending, and peer-to-peer lending, is also gaining popularity among small businesses. This occurs through online platforms that use technology to bring together borrowers underserved by traditional lending institutions with loan investors seeking high-yield-generating investments. Alternative lenders usually have shorter applications with fewer requirements, making alternative lending an excellent opportunity for lending businesses seeking new opportunities and for borrowers looking for alternative borrowing solutions.
Even traditional banks are now looking to explore non-traditional sources of financing. At the latest investor day at JP Morgan Chase, private credit is one of the areas where the bank sees an opportunity for growth in commercial and investment banking. Jamie Dimon, chairman and chief executive of the bank, said the bank would compete in private credit.
Additionally, Jennifer Piepszak, Co-CEO of Commercial & Investment Bank at JP Morgan, mentioned, "The competitive landscape for our businesses continues to intensify from traditional peers in areas like Middle Market and Investment Banking, as well as non-banks in areas like Private Credit." Troy Rohrbaugh, Co-CEO of Commercial & Investment Bank, added that the bank is the largest financier of private credit portfolios and will remain a significant player. In addition, the bank already has dedicated capital on its balance sheet to put to work on direct loans for corporate borrowers.
3. Tougher market conditions drive more strict regulatory supervision
Banks have faced increased regulatory supervision since the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank in March 2023. In 2024, the intensity of supervision and regulation continues with reviews and examinations done more frequently, faster response time for issues and escalations, and an increased focus on risk management and governance. Banks have been compelled to reassess their operations, risk management policies, governance and controls, and data and systems infrastructure. Expanded regulatory coverage, innovative technologies, rapidly evolving products and services, growing interconnectedness, and the global political environment are contributing to heightened supervision and examination at the state, federal, and international levels, significantly enhancing the complexity of regulatory compliance.
Stuart Plesser, Financial Institutions Managing Director at S&P Global Ratings, views tougher regulation and supervision as a net positive for creditors. Tighter oversight of capital, liquidity, interest-rate risk, and other factors support creditworthiness. On the downside, stricter regulatory requirements carry costs and can affect banks' appetites to lend. If banks become more selective in lending to preserve their balance sheets and look to comply with more stringent proposed regulations, entities such as small and medium-sized businesses, as well as households, could find it incrementally harder to gain funding. That may also open further room for non-banks to compete.
Additionally, as technology advances, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into financial systems makes compliance programs even more challenging. Regulators are closely monitoring the impact of AI on anti-money laundering (AML) efforts, acknowledging the benefits of innovation coupled with the required risk management.
4. Traditional Banks are focusing on meeting sustainable development financing targets
While transitioning into the customer-centric space, the banks must also cope with borrowers' increasing demand for loans with a positive environment, social, and corporate governance (ESG) impact. Over the last few years, sustainability-linked loans have become popular - these are loans for general corporate purposes, and the usage of proceeds is not limited to funding green initiatives. Instead, the loans periodically track specified sustainability-based key performance indicators (KPIs). In lending, offering sustainability-linked loans, investing in ESG-friendly technology, and being transparent about an organization's efforts towards issues such as carbon emission or gender wage gaps can help banks gain a competitive advantage.
All banks are following up on their Sustainable Finance strategy, recognizing the scale and urgency of climate change. JP Morgan facilitated over $200 billion in green financing initiatives, including renewable energy projects and green bonds, contributing to its ambitious $2.5 trillion sustainable development financing target by 2030.
Goldman Sachs aims to deliver $750 billion in sustainable financing, investing, and advisory activities. Moreover, in February 2024, Goldman Sachs Asset Management launched the Global Green Bond ETF (exchange-traded fund). Hilary Lopez, Head of EMEA Third Party Wealth at Goldman Sachs Asset Management, said, "The global green bond market offers increasing opportunities for investors seeking to complement their fixed income exposure with dedicated green, social, and impact bonds," This was the first launch of an ETF format, the bank plans to continue expanding its product range to support its clients' investment and sustainability objectives.
S&P Global Ratings anticipates that despite global macroeconomic uncertainty in key regions, green, social, and sustainability-linked (GSSS) bond issuance will increase modestly to $0.95-$1.05 trillion in 2024, from $0.98 trillion in 2023. Green bonds will continue to dominate GSSS bond markets, boosted by increased demand for environmental projects across all geographies.

Conclusion
Apart from these key trends impacting the U.S. lending industry, other factors such as emphasis on excellent customer service and fostering strong client relationships have become predominant. These will serve as a foundation for long-term success; hence, innovation, both in product offerings and services, will provide a competitive advantage to the banks. Additionally, the banks must accept digital lending solutions as they emerge with transformative strategies that deliver efficiency gains and enhanced customer experiences.
For the rest of 2024, demand for loans across all categories (commercial, industrial, and consumer loans) in the U.S. is expected to be modest, given the current macroeconomic conditions and high borrowing costs. Banks are likely to continue with their restrictive lending policies, and the tightened credit standards are also likely to prevail across all loan categories. However, as soon as the U.S. macroeconomic environment becomes favorable and the Fed starts cutting interest rates, the situation is expected to improve later in 2024.
How Evalueserve can support
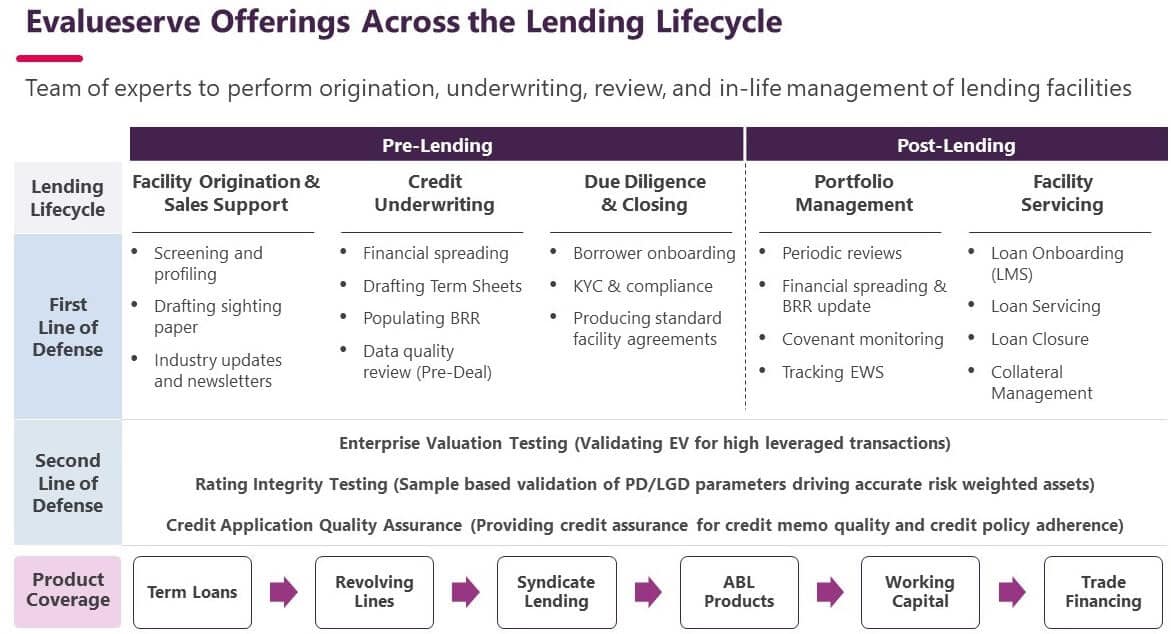
We partner with corporate and commercial banks to improve efficiency and accuracy and meet the demands of a changing market and heightened regulatory scrutiny. Our tech-enhanced services combine domain expertise with technology accelerators, such as AI-powered Spreadsmart, to help banks make faster, smarter credit decisions. We support major banks around the globe with solutions across the lending lifecycle, including:
Check out our blog 2024 Trends in European Corporate and Commercial Lending.
Talk to One of Our Experts
Get in touch today to find out about how Evalueserve can help you improve your processes, making you better, faster and more efficient.


